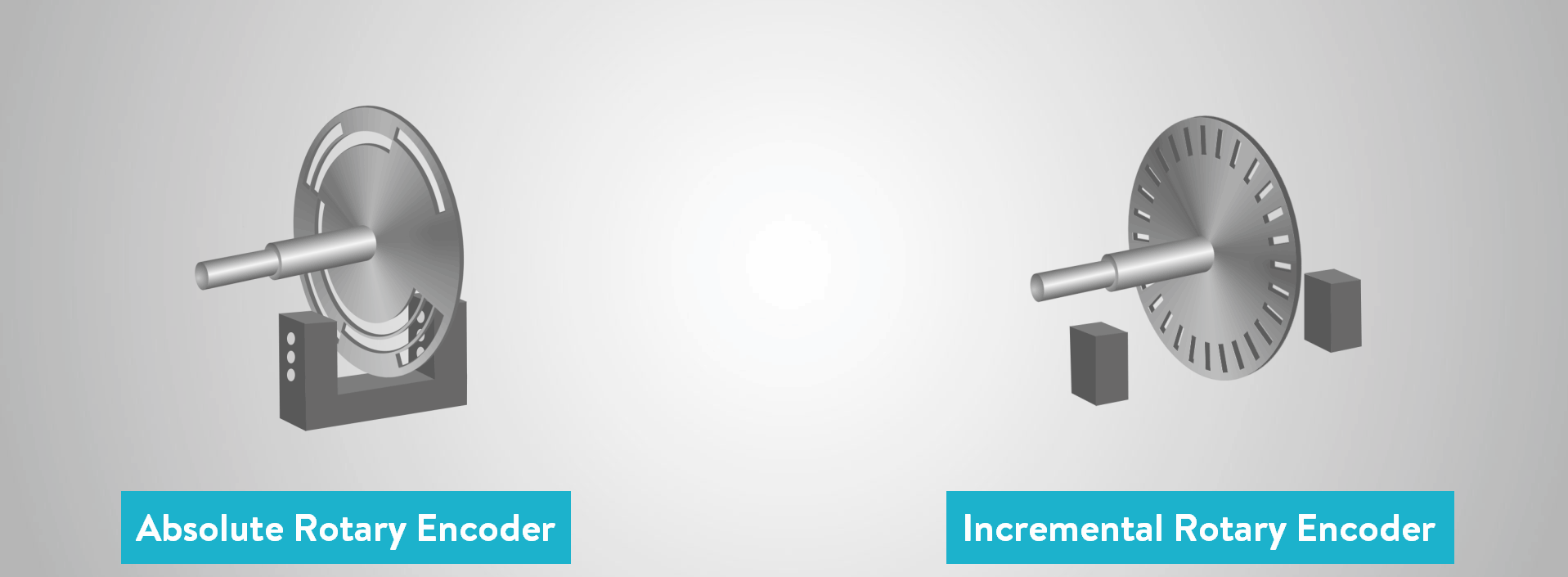
In motion control systems, selecting the right encoder is crucial for ensuring accuracy, reliability, and efficiency. With various types available, absolute and incremental encoders, understanding their differences and knowing when to use each can significantly impact system performance and cost-effectiveness.
Consideration Factors When Selecting between Absolute and Incremental Encoders
1. Position Tracking Requirements
One of the main factors is how your system tracks position. Different encoder types offer varying levels of precision and data retention.
- Absolute Encoders provide a unique digital value for each shaft position, even after power loss. This makes them ideal for applications where knowing the exact position at all times is critical, such as in robotics, medical devices, or automated assembly lines. They eliminate the need for re-homing and ensure consistent performance.
- Incremental Encoders generate pulses as the shaft rotates, which are counted to determine relative position. They are more cost-effective and suitable for applications where relative movement tracking is sufficient, such as conveyor systems, motor feedback, or basic automation tasks.
2. Power Loss Recovery
Power interruptions can significantly impact encoder performance, especially in systems that require continuous and accurate position awareness. The ability of an encoder to retain or recover position data after a power outage is a key consideration in many industrial and automation applications.
- Absolute Encoders retain position data even when power is lost. This is because each position corresponds to a unique digital code, allowing the system to resume operation immediately without the need for recalibration or re-homing. This feature makes absolute encoders ideal for mission-critical systems, such as robotics or medical devices, where downtime must be minimised and precision is essential.
- Incremental Encoders, in contrast, lose their position reference when power is interrupted. Since they rely on counting pulses to determine position, any loss of power resets the count. Upon restart, the system must be re-homed or recalibrated to re-establish the correct position, which can lead to operational delays and increased maintenance time, especially problematic in high-throughput or safety-sensitive environments.
3. Resolution and Accuracy
The level of precision required by your application will influence your encoder choice. Resolution determines how finely position can be measured, while accuracy reflects how close the measured position is to the true position.
- Absolute Encoders offer high resolution and exceptional accuracy. Each position is represented by a unique digital code, allowing precise and unambiguous position tracking. Advanced models can provide multi-turn data, making them ideal for complex motion systems such as robotic arms, CNC machines, and automated inspection equipment. Their ability to deliver exact position data without needing a reference point makes them indispensable in high-precision applications.
- Incremental Encoders provide resolution based on the number of pulses per revolution (PPR). While they can achieve good precision, they only track relative movement and require a homing sequence to determine absolute position. This makes them suitable for moderate-precision tasks like motor speed control, conveyor systems, and general automation, where cost-efficiency and simplicity are more important than ultra-high accuracy.
4. Application Environment
Environmental conditions such as temperature, vibration, dust, and moisture can significantly affect encoder performance and reliability. Choosing the right encoder type depends on the operating environment and the criticality of the application.
- Absolute Encoders are designed for reliability in harsh or safety-critical environments. Their robust construction and ability to retain position data make them suitable for use in aerospace, medical devices, and heavy industrial machinery. They perform well under extreme conditions, including high vibration, temperature fluctuations, and contamination, ensuring consistent operation even in demanding settings.
- Incremental Encoders are commonly used in standard industrial environments where conditions are relatively controlled. They offer a good balance between performance and cost, making them ideal for packaging machines, printing presses, and general-purpose automation. However, in harsher environments, they may require additional protective measures such as sealed housings or environmental enclosures to maintain performance and longevity.
5. Speed Response
In fast-moving machines or systems, it’s important for the encoder to keep up and provide quick, accurate feedback. This helps the system stay in control and avoid errors during high-speed operations.
- Absolute Encoders are well-suited for high-speed tasks. They can instantly report the exact position without needing to count steps or reset. This makes them ideal for fast and precise systems like robotic arms, automated pick-and-place machines, or high-speed sorting equipment. Because they always know the position, they help the system respond quickly and smoothly, even during rapid movements.
- Incremental Encoders can also work in fast-moving systems, but they rely on counting pulses to track movement. At very high speeds, there’s a risk that some pulses might be missed if the system can’t process them quickly enough. This can lead to small errors or delays. While they’re still used in many fast applications, they may need extra electronics or careful setup to make sure they stay accurate when things move quickly.
Choosing the right encoder involves more than just selecting a product, it’s about matching the encoder’s capabilities to your system’s specific needs. Whether you require high-resolution feedback, robust performance in harsh conditions, or cost-effective motion tracking, understanding the strengths of absolute and incremental will help you make the best choice. Learn more about the differences between absolute and incremental encoders.
At Transtech, we offer a wide range of motion control products such as heavy duty and industrial encoders from world-leading supplier such as Baumer-Hubner.
If you’re unsure which encoder suits your application, contact us and our team of specialists can guide you through the selection process or even customise a solution tailored to your operational requirements.